
Note:
This is not a generic NCERT summary. All the points written here are carefully curated for the sake of acting as a precise guide for all three stages of UPSC: Prilims, Mains and Interview. The meanings of the most basic words are often asked in the Interview before asking a question about how the candidate would go about solving that issue.
Ex: Explain what prejudice means. Then, Should we eradicate the Stereotypes? or Can the stereotypes be sometimes good?
As a general rule of thumb, use the Concepts section for answer writing and interviews and Facts section for Prilims.
Chapter 1 – Understanding Diversity
The only alternative to coexistence is co-destruction
Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first prime minister
Concepts:
- The concept of difference vs. inequality is introduced. There are differences in cultures, languages spoken and food people eat across India. These are an aspect of Diversity. But inequality is a state where a person doesn’t have resources and opportunities that another person does.
- Diversity adds meaningful value to our lives by enriching our perspectives and refining our lens through which we see the world.
- Historical and geographical factors influence the diversity of a region. Food the people living there eat, clothes they wear and the kind of work they do. To illustrate this point, a case study of Ladakh and Kerala is given. Differences are mentioned in the facts section.
Facts:
- Samir is an other name for Lord Hanuman’s father.
- Unity in Diversity is a phrase coined by Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru.
| Ladakh | Kerala |
| Desert area, less rain | Coastal area |
| East of Jammu Kashmir | South west corner of India |
| Pashmina shawls are made from the sheep and goat | Spices are cultivated due to attractive agricultural prospects |
| Eat meat and milk products | |
| Budhism reached Tibet via Ladakh, hence it’s called little Tibet | Vasco de gamma landed here when Portugese discovered the sea route to India |
Chapter 2 – Diversity and Discrimination
Collective fear stimulates herd instinct, and tends to produce ferocity toward those who are not regarded as members of the herd.
Bertrand Russell, Unpopular Essays
Concepts:
- Prejudice is a preconceived opinion that is not based on reason or actual experience. People can be prejudiced against many things: religious beliefs, color of the skin etc.,
- Stereotype is an oversimplified image or idea of a particular type of person or thing.
- Discrimination happens when people act on their stereotypes or prejudices.
Facts:
- In India, we have more than 1600 languages that are mother tongues.
- The term Dalit means ‘broken’.
Chapter 3 – Government
The care of human life and happiness, and not their destruction, is the first and only object of good government
Thomas Jefferson
Concepts:
- A Government is the system or group of people administering a society
- There are three levels of government in India: Local, State and Central. There are also different types of government such as Democratic, Monarchic etc.,
Facts:
- On June 2nd, 2014 Telangana became a separate state after reorganization of Andhra Pradesh
- On Oct 31st, 2019, Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two union territories, J&K and Ladakh.
- American women got the right to vote in 1920 and UK women got their right to vote after a few years in 1928
Chapter 4 – Key Elements of a Democratic Government
The care of human life and happiness, and not their destruction, is the first and only object of good government
Thomas Jefferson
Concepts:
- Key elements that influence the working of a Democracy are the people’s participation, the government’s participation in resolution of conflict and government’s commitment towards equality and justice.
- People participate directly through elections and sometimes indirectly through rallies, exercising their right to criticize etc.,
- Resolution of conflict arises for multiple reasons. An example if of the river Kaveri that flows from Karnataka and Tamilnadu. They both have dams Krishnaraja and Mettur as shown in the pic below. If the flow of water is blocked at the upstream, the Tamilnadu doesn’t get enough water. A good Democracy has the need to resolve conflicts.
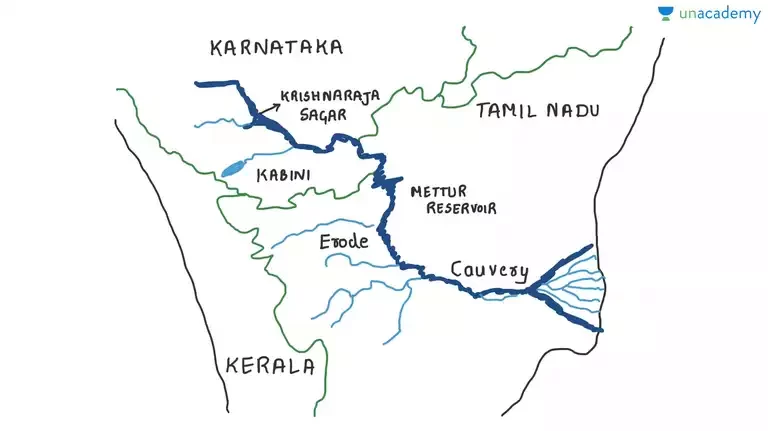
- Democracy also has its commitment towards providing equality and justice. They’re inseparable.
Facts:
- None in this chapter.
Chapter 5 – Panchayati Raj
Concepts:
- A Government is the system or group of people administering a society
- There are three levels of government in India: Local, State and Central.
- Panchayati Raj is a system of local government in India.
- Panchayat is an elective council in rural areas in India.
- Gram Sabha is a meeting of all people who live in an area covered by a Panchayat. This could be one village or multiple.
- Anyone who is 18 years old or more and who has the right to vote is a member of the Gram Sabha.
- Each village panchayat has wards and people living in it elect a ward member (Panch). They also elect a Sarpanch who is the Panchayat President. Panchs and Sarpanch together form Gram Panchayat which is elected for 5 years.
- GP also has a secretary who is also secretary of Gram Sabha. They’re responsible for calling a meeting and keeping the proceedings of them.
- Gram Panchayat are answerable to the Gram Sabha because it is the members of the Gram Sabha who elected them
- People’s participation in rural areas can also be seen in block level (Janpad Panchayat or Panchayat Samiti) and above that is Zilla Parishad which handles district level developmental plans.
Facts:
- Two village Panchs from Maharashtra who were awarded the Nirmal Gram Puruskar in 2005 for the excellent work done by them in the Panchayat
- On June 2nd, 2014 Telangana became a separate state after reorganization of Andhra Pradesh.
- On Oct 31st, 2019, Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two union territories, J&K and Ladakh.
- American women got the right to vote in 1920 and UK women got their right to vote after a few years in 1928.
Chapter 6 – Rural Administration
Concepts:
- Usually in the rural areas, the land is measured and the records are kept by Patwaris. They are called by different names in different places like Karamchari, Village officer etc.,
- In India all the states are divided into districts and districts into sub-divisions that are called Tehsil, Taluka etc., The head of the district is District Collector and under them are revenue officers called Tehsildars. They supervise the work of Patwaris.
Facts:
- Hindu Succession Amendment Act was passed in 2005 to make sure that Hindu women too get their fair share of land as their men counterparts at the time of property inheritance.
Chapter 7 – Urban Administration
Concepts:
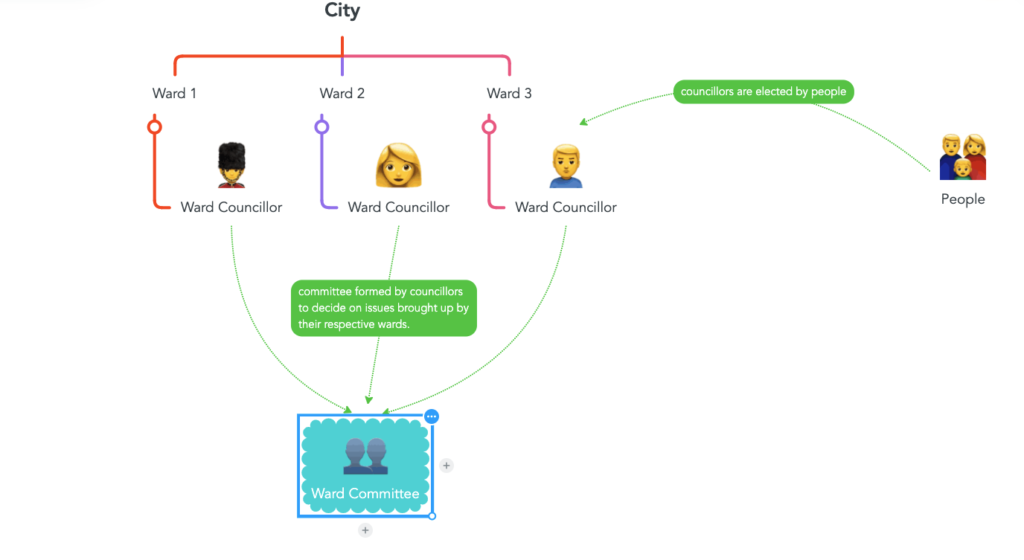
- Commissioner and administrative staff are responsible for implementation of the issues decided by the ward committees and they are appointed unlike councillors who are elected.
Facts:
- N/A
Chapter 8 – Rural Livelihoods
Concepts:
- Mostly narratives about different kinds of people living in rural areas and occupations are given. Fishing in coastal areas, farming in rural areas, selling honey etc are the primary and additional sources of income in rural areas.
Facts:
- In India 80% farmers do not own enough land to cultivate and make their ends meet which is why they often work on other people’s land for a daily wage.
Chapter 9 – Urban Livelihoods
Concepts:
- Mostly narratives about different kinds of people living in urban areas and occupations are given. Selling products on the streets, manufacturing etc., It also described harsh working conditions of people and about “seasonal” workers who can be hired and fired at anytime.
Facts:
- In a survey done in Ahmedabad city, it was found that 12% of all the workers were the people working on streets. They sell something or provide required services to the people.
- There are almost 1 crore street vendors in the country working in urban areas.